For HDDs, the lifespan is typically estimated based on the MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) metric, which is the average time between failures. Consumer-grade HDDs usually have an MTBF of around 1 to 2 million hours, which translates to a lifespan of around 3 to 5 years with regular usage. Enterprise-grade HDDs can have a longer lifespan of around 5 to 10 years.
For SSDs, the lifespan is typically estimated based on the TBW (Terabytes Written) metric, which is the total amount of data that can be written to the drive before it fails. Consumer-grade SSDs usually have a TBW of around 150 to 600 terabytes, which translates to a lifespan of around 3 to 5 years with regular usage. Enterprise-grade SSDs can have a longer lifespan of around 5 to 10 years.
Table of Contents
ToggleSSD and HDD
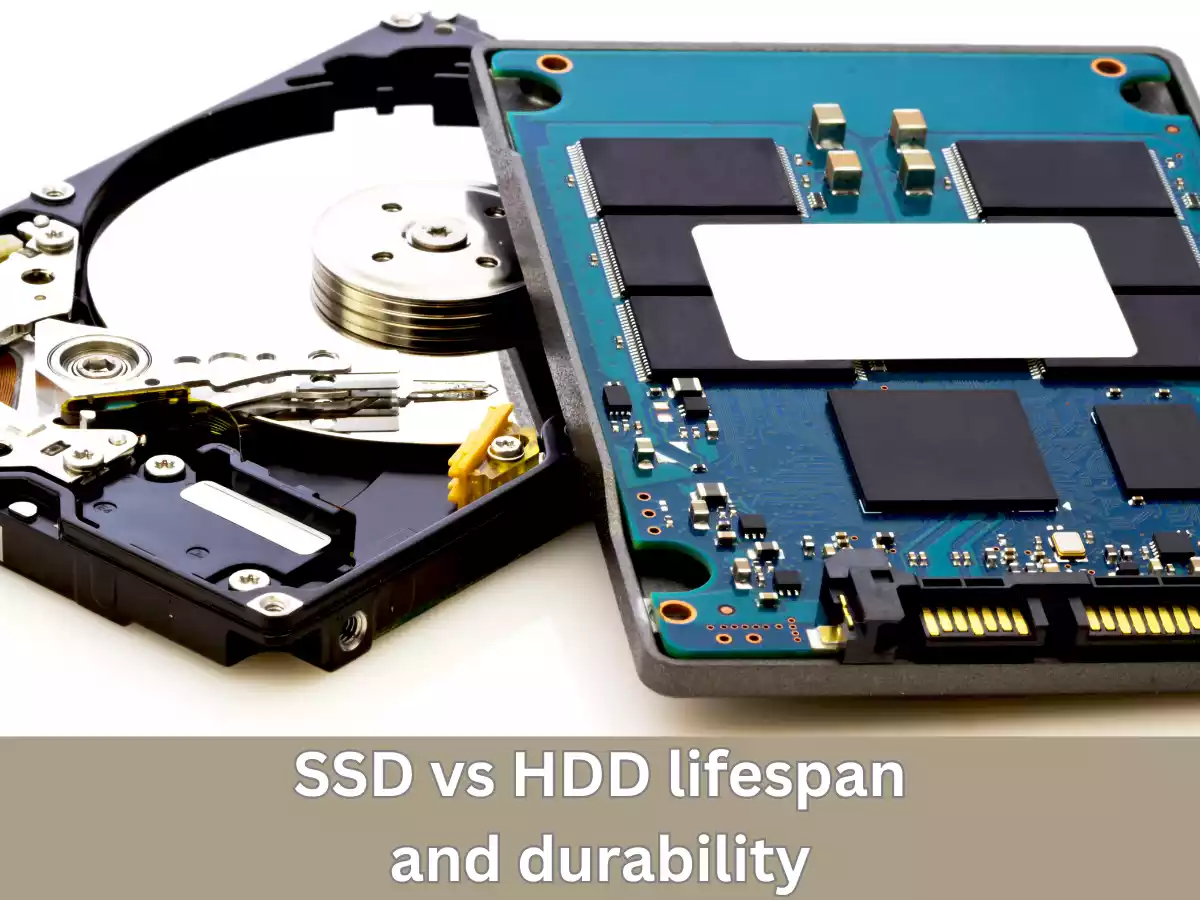
SSD (Solid State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disk Drive) are both types of computer storage devices used to store digital data, such as operating systems, software programs, documents, media files, and more.
An HDD uses magnetic disks and a read/write head to read and write data. It is the older and more traditional storage device that has been in use for several decades. On the other hand, an SSD uses NAND-based flash memory to store data, making it faster, lighter, and more durable than an HDD.
Both SSD and HDD have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on various factors, such as cost, performance, capacity, and durability.
Importance of lifespan and durability of storage devices
The lifespan and durability of storage devices are critical factors in determining the overall performance and reliability of a computer system.
A storage device’s lifespan refers to the length of time it can be used before it starts to fail or become unreliable, while durability refers to the device’s ability to withstand physical wear and tear, environmental factors, and other external forces that could damage it.
If a storage device has a short lifespan or is not durable, it can lead to data loss, system crashes, and other technical issues. This can result in significant downtime, loss of productivity, and financial loss for individuals and businesses. Therefore, it is crucial to choose storage devices with a longer lifespan and greater durability to ensure optimal system performance and data safety.
Advantages and disadvantages of SSD and HDD
Advantages of SSD
- Faster read/write speeds than HDDs, leading to faster boot and load times
- Lightweight and durable, making them ideal for laptops and portable devices
- No moving parts, reducing the risk of physical damage or mechanical failure
- More energy-efficient, leading to longer battery life for laptops.
- Quieter operation than HDDs
Disadvantages of SSD
- Higher cost per GB compared to HDDs
- Reduced performance as the drive fills up
- Difficulty in recovering data if the drive fails
Advantages of HDD
- Lower cost per GB compared to SSDs
- Higher capacity options available
- Easy to recover data from failed drives
- Widely compatible with most computer systems
Disadvantages of HDD
- Slower read/write speeds than SSDs, leading to slower boot and load times
- Heavier and less durable than SSDs
- Mechanical components increase the risk of physical damage or mechanical failure
- Energy-intensive, leading to higher power consumption and shorter battery life for laptops
- Louder operation than SSDs
Factors affecting the lifespan of SSD and HDD
There are several factors that can affect the lifespan of both SSD and HDD, including:
Type of usage: Frequent read/write operations, heavy workloads, and continuous use can reduce the lifespan of both SSD and HDD.
Temperature: High temperatures can shorten the lifespan of both SSD and HDD, as they can cause damage to the electronic components or mechanical parts.
Manufacturing quality: The quality of the components, production process, and quality control can affect the lifespan of both SSD and HDD.
Age: The age of the storage device can also impact its lifespan, as wear and tear accumulate over time.
Power failures and voltage fluctuations: Power failures or sudden voltage fluctuations can damage the electronic components or mechanical parts of both SSD and HDD, reducing their lifespan.
Environmental factors: Exposure to dust, moisture, humidity, and other environmental factors can cause damage to both SSD and HDD.
Firmware updates: Firmware updates can sometimes cause unexpected issues that may affect the lifespan of SSD and HDD.
It is important to take care of storage devices by ensuring proper usage, maintaining optimal operating temperatures, avoiding power failures, and protecting them from environmental factors to prolong their lifespan.
Estimated lifespan of SSD and HDD
The estimated lifespan of both SSD and HDD depends on various factors, including usage patterns, manufacturing quality, and environmental conditions.
For HDDs, the lifespan is typically estimated based on the MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) metric, which is the average time between failures. Consumer-grade HDDs usually have an MTBF of around 1 to 2 million hours, which translates to a lifespan of around 3 to 5 years with regular usage. Enterprise-grade HDDs can have a longer lifespan of around 5 to 10 years.
For SSDs, the lifespan is typically estimated based on the TBW (Terabytes Written) metric, which is the total amount of data that can be written to the drive before it fails. Consumer-grade SSDs usually have a TBW of around 150 to 600 terabytes, which translates to a lifespan of around 3 to 5 years with regular usage. Enterprise-grade SSDs can have a longer lifespan of around 5 to 10 years.
It is important to note that these estimates are based on average usage patterns and environmental conditions, and individual results may vary. Proper maintenance and care can help to prolong the lifespan of both SSD and HDD.
Definition of durability in the context of storage devices
In the context of storage devices, durability refers to the ability of the device to withstand various types of stress and wear and tear over time. It involves the ability to maintain functionality and performance despite exposure to external factors such as temperature, humidity, shock, and vibration.
A durable storage device is designed to withstand harsh environments and heavy usage, ensuring that it can provide reliable storage for an extended period. This is particularly important in industries such as aviation, transportation, and industrial automation, where storage devices may be subjected to extreme conditions and need to function reliably in critical applications.
Durability can also be a consideration for personal use, as storage devices are often used in portable applications where they may be exposed to rough handling or extreme temperatures. In these cases, a more durable storage device can help to ensure that data is protected and the device lasts longer.
Comparison of durability between SSD and HDD
When it comes to durability, SSDs have several advantages over HDDs:
No moving parts: SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them less susceptible to damage from shock, vibration, or other physical stresses that can damage HDDs.
Resistance to heat and cold: SSDs are more resistant to temperature extremes than HDDs, which can cause mechanical parts to expand and contract and lead to premature failure.
Better resistance to moisture and humidity: SSDs are less likely to be affected by moisture and humidity than HDDs, which can damage the delicate moving parts in an HDD.
Better shock resistance: SSDs can withstand more shock and impact than HDDs, which can cause damage to the spinning platters in an HDD.
Lower power consumption: SSDs require less power than HDDs, which can reduce the risk of power-related failures.
However, there are also some potential durability concerns with SSDs:
Limited write cycles: SSDs have a limited number of write cycles before they begin to fail. Overuse of an SSD can lead to premature failure, especially in consumer-grade models.
Susceptibility to power loss: SSDs are vulnerable to power loss, which can cause data corruption or loss if data is being written at the time of power loss.
Overall, while SSDs have some advantages in terms of durability, they are not invulnerable to failure, and the lifespan of an SSD depends on various factors, including usage patterns, manufacturing quality, and environmental conditions. HDDs have a longer history of reliable operation, but they are more vulnerable to mechanical failure and environmental factors.
How to prolong the lifespan and improve the durability
Here are some ways to prolong the lifespan and improve the durability of both SSD and HDD:
Use a high-quality device: Investing in a high-quality storage device can improve its durability and reliability. Look for devices with strong construction, high-quality components, and a solid reputation for reliability.
Keep them cool: Both SSD and HDD can be sensitive to temperature, so keep them in a cool, well-ventilated environment. Avoid placing them in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
Keep them clean: Dust and debris can accumulate on the surface of SSD and HDD, which can cause damage. Use a soft, dry cloth to clean them regularly.
Protect them from physical damage: Both SSD and HDD can be sensitive to physical damage, so handle them with care. Avoid dropping or jarring them, and use protective cases for portable drives.
Use a UPS: Power failures and voltage fluctuations can damage SSD and HDD, so use an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to protect them.
Keep them clean: Dust and debris can accumulate on the surface of SSD and HDD, which can cause damage. Use a soft, dry cloth to clean them regularly.
Update firmware: Keep the firmware of your SSD and HDD up to date, as it can improve performance and fix bugs that may cause issues.
Use backup and redundancy: Backing up your data regularly and using redundancy can help to ensure that your data is protected in case of device failure.
Monitor usage: Keep an eye on how much data you are writing to your SSD and HDD. Tools like Resource Monitor on Windows or Activity Monitor on Mac can help you track usage and avoid overloading the drives.
By following these tips, you can help to improve the durability and reliability of your SSD and HDD, reduce the risk of data loss, and ensure optimal system performance.
Cost comparison between SSD and HDD
When it comes to cost, HDDs are generally less expensive than SSDs. This is because HDDs have been on the market for much longer and are produced in larger quantities, resulting in economies of scale that make them more affordable.
In addition, the cost per gigabyte of storage is typically lower for HDDs than for SSDs. This means that for large storage needs, HDDs can be a more cost-effective choice.
However, the cost difference between SSDs and HDDs has been decreasing in recent years, as the demand for SSDs has increased and production costs have come down. As a result, the price gap between the two types of drives is smaller than it used to be, and SSDs are becoming more affordable for mainstream consumers.
While SSDs may be more expensive than HDDs on a per-gigabyte basis, they do offer advantages in terms of performance, durability, and energy efficiency, which can make them a better value in the long run. When making a purchasing decision, it’s important to consider your specific needs and budget, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of each type of drive.
Performance comparison between SSD and HDD
When it comes to performance, SSDs have several advantages over HDDs:
Faster read and write speeds: SSDs can read and write data much faster than HDDs, resulting in faster boot times, application loading times, and file transfers.
Lower latency: SSDs have lower latency than HDDs, which means that data can be accessed more quickly and efficiently.
Better random access performance: SSDs can access data randomly, which means that they can retrieve small pieces of data quickly, while HDDs have to search for the data on spinning platters.
No fragmentation: SSDs don’t suffer from fragmentation like HDDs, which can slow down access times as the drive has to search for scattered data on the platters.
Energy efficiency: SSDs require less power than HDDs, which can result in longer battery life for portable devices and lower power bills for desktops.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to SSDs in terms of performance:
Limited write cycles: SSDs have a limited number of write cycles before they begin to fail. Overuse of an SSD can lead to slower write speeds and a shorter lifespan.
Susceptibility to power loss: SSDs are vulnerable to power loss, which can cause data corruption or loss if data is being written at the time of power loss.
Overall, while SSDs have some advantages in terms of performance, their performance may be impacted by usage patterns, manufacturing quality, and other factors. HDDs have a longer history of reliable operation, but they are slower and less energy-efficient than SSDs. When considering performance, it’s important to consider your specific needs and use case, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of each type of drive.
Choosing between SSD and HDD based on lifespan and durability
When choosing between SSD and HDD based on lifespan and durability, here are some recommendations to consider:
Consider your usage patterns
If you plan to use your storage device for tasks that require frequent writes, such as video editing or gaming, an SSD may be a better choice due to its faster write speeds and durability. However, if you plan to use your storage device for less demanding tasks, an HDD may be a more cost-effective option.
Consider your budget
SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs, so if budget is a concern, an HDD may be a more affordable option.
Consider physical wear and tear
If you plan to use your storage device in a mobile device or a location where it may be subject to physical shock or vibration, an SSD may be a better choice due to its resistance to such factors.
Consider the importance of backup and data protection
Regardless of whether you choose an SSD or HDD, it’s important to regularly back up your data to protect against data loss in case of device failure or other issues.
Ultimately, the choice between an SSD and HDD for lifespan and durability will depend on your specific needs and budget. It’s important to consider both cost and performance, as well as the factors that may impact the lifespan and durability of each type of device, before making a decision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between an SSD and HDD based on lifespan and durability depends on a variety of factors such as usage patterns, budget, physical wear and tear, and data protection needs. While SSDs offer several advantages over HDDs in terms of durability and lifespan, such as resistance to physical shock and vibration and a lack of mechanical parts, they can be more expensive and have limited write endurance. HDDs, on the other hand, are generally more affordable and have a longer track record of reliable operation, but are more vulnerable to physical damage and slower than SSDs.
Regardless of the type of storage device chosen, it’s important to take steps to protect and maintain the device over time, such as backing up data regularly, keeping the device cool and clean, and avoiding physical damage. By considering the specific needs and use case, as well as both cost and performance, users can make an informed decision when choosing between an SSD and HDD for lifespan and durability.